REPORT
Tuberculosis in the City & County of San Francisco, 2024
The mission of San Francisco Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Program is to control, prevent, and finally eliminate tuberculosis in San Francisco by providing compassionate, equitable, and supportive care of the highest quality to all persons affected by this disease. In 2022, 57 new cases with active tuberculosis (TB) were reported in San Franciscans (6.9 cases per 100,000 persons). The rate of TB in San Francisco is nearly triple the national rate of 2.5 cases per 100,000 persons, and 1.5 times the California rate of 4.7 cases per 100,000 persons.
In 2024, 91 new cases with active tuberculosis (TB) were reported in San Francisco (10.9 cases per 100,000 persons). The rate of TB in San Francisco is more than three times the national rate of 3.0* cases per 100,000 persons and twice the California rate of 5.4 cases per 100,000 person.

Demographics
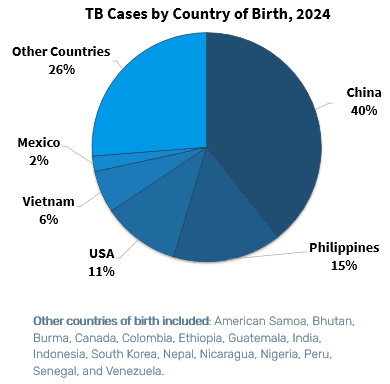
In 2024, among San Francisco residents, 81 cases were reported among non-U.S.-born residents for an incidence rate of 27.5 cases per 100,000 persons, compared with 10 cases among U.S.-born residents for an incidence rate of 1.8 cases per 100,000 persons.
In terms of race/ethnicity, Asian/Pacific Islander residents had the highest TB incidence rate (22.6 cases per 100,000 persons), which was over 30 times the rate among Non-Hispanic White residents (0.7 cases per 100,000 persons).
Incidence rates were 17 times higher among Hispanic/Latino residents (11.7 cases per 100,000 persons) and nearly 20 times higher among NonHispanic Black residents (13.6 cases per 100,000 persons) compared with Non-Hispanic White residents.


Site of Disease
In 2024, 61 cases were pulmonary TB, 16 were extrapulmonary TB, and 14 were both pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB.
Extrapulmonary TB sites included lymph nodes, joint, pleural, spine, eye, skin, meningeal, gastrointestinal, peritoneal, and genitourinary system.
Comorbidities and Risk Factors
Among residents with a reported case of TB, 65 (71%) had at least one comorbid medical condition, and 42 (46%) residents had two or more comorbidities.
The most common medical risk factors among residents with TB were smoking 37 (41%), diabetes mellitus 19 (21%), and immunocompromised status 12 (13%) including HIV 2 (2%).
Age at Report Time
Among 91 cases reported in 2024, 37 (41%) were identified in male residents. The median ages in years at time of TB reporting was 64 (range: 0-94). One pediatric case (0-14) was reported, and nearly half (48%) of reported cases were in individuals ages 65 and older.

Mortality
At the time of this publication, 10 (11%) residents with TB reported in 2024 died. Two had died prior to TB diagnosis.
Drug Resistance to Standard Medications
In 2024, the proportion of TB cases with any drug resistance was low 7/91 (8%). There were six cases with drug resistance to first-line TB medications, and one case of multidrugresistant (MDR) TB was reported. MDR TB is TB resistant to the two most potent first line drugs, isoniazid and rifampin
